Cryptocurrency vs. Fiat: The Ultimate Guide for US Investors
In the ever-evolving landscape of finance, two dominant forms of currency stand out: cryptocurrency and fiat currency. For investors in the USA, understanding the fundamental difference between cryptocurrency and fiat currency is not just academic; it’s crucial for navigating the modern economic world. Imagine a world where your money isn’t controlled by a central bank, but by a decentralized network of computers. This is the promise of cryptocurrency, a stark contrast to the traditional dollars and cents we’ve grown up with. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of both, helping you make informed decisions about your financial future.
What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency, often simply called ‘crypto,’ is a digital or virtual currency secured by cryptography, making it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Unlike traditional money, cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning they are not subject to government or central bank control. Bitcoin, launched in 2009, was the first and remains the most well-known cryptocurrency. Its underlying technology, blockchain, is a distributed public ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This transparency and immutability are core to crypto’s appeal.
What is Fiat Currency?
Fiat currency is government-issued money that is not backed by a physical commodity, such as gold or silver. Its value is derived from government decree (fiat) that it is legal tender, and the public’s trust in the issuing government. The U.S. Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, and British Pound are all examples of fiat currencies. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the USA, manage the supply of fiat currency, influencing its value through monetary policy, interest rates, and quantitative easing.

How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
At its core, cryptocurrency operates on a technology called blockchain. Imagine a digital ledger that is distributed across thousands of computers worldwide. Every time a transaction occurs, it’s added as a ‘block’ to this chain. Once a block is added, it cannot be altered, creating an immutable and transparent record. This decentralized nature means no single entity controls the network, making it resistant to censorship and manipulation. Users typically interact with cryptocurrencies through digital wallets, which store their private keys and allow them to send and receive funds. Mining, or staking, are processes by which new coins are created and transactions are validated, incentivizing participants to maintain the network’s integrity.
How Does Fiat Currency Work?
Fiat currency functions within a centralized system. Governments and central banks control its issuance, distribution, and regulation. When you use fiat currency, whether it’s cash or a digital transfer, you’re relying on the banking system to facilitate the transaction. Banks act as intermediaries, verifying identities and maintaining records. The value of fiat currency is influenced by a country’s economic stability, government policies, and market demand. Central banks use various tools, such as adjusting interest rates and controlling the money supply, to manage inflation and stimulate economic growth. This centralized control allows for greater stability and easier implementation of economic policies, but also introduces the risk of government overreach or mismanagement.
Benefits and Use Cases
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies offer several compelling benefits and use cases, particularly for those seeking alternatives to traditional financial systems:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, reducing the risk of censorship or manipulation.
- Transparency and Immutability: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger (blockchain) and cannot be altered, fostering trust.
- Lower Transaction Fees: For international transfers, crypto can often be cheaper and faster than traditional banking.
- Financial Inclusion: Provides access to financial services for the unbanked or underbanked population globally.
- Innovation: Powers new technologies like Decentralized Finance (DeFi), NFTs, and Web3 applications.
- Potential for High Returns: While volatile, some cryptocurrencies have seen significant price appreciation, attracting investors.
Fiat Currency
Despite the rise of crypto, fiat currency remains the backbone of the global economy due to its inherent advantages:
- Stability and Acceptance: Widely accepted for goods and services, and its value is generally more stable due to government backing and regulation.
- Legal Tender Status: Legally recognized for all debts, public and private, ensuring its universal acceptance.
- Government Backing: Supported by the full faith and credit of a government, providing a sense of security.
- Monetary Policy Control: Central banks can implement policies to manage inflation, stimulate growth, and stabilize the economy.
- Consumer Protection: Established regulatory frameworks offer consumer protection and recourse in case of fraud or disputes.
- Ease of Use: Familiarity and widespread infrastructure make it easy to use for everyday transactions.
Common Risks or Drawbacks
Cryptocurrency
While offering exciting possibilities, cryptocurrencies come with their own set of risks:
- Volatility: Prices can fluctuate wildly, leading to significant gains or losses in a short period.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The regulatory landscape is still evolving, creating legal and operational risks.
- Security Risks: Vulnerability to hacks, scams, and phishing attacks, leading to loss of funds.
- Scalability Issues: Some blockchains struggle with transaction speed and volume, leading to network congestion and high fees.
- Environmental Concerns: The energy consumption of some proof-of-work cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin) is a growing concern.
- Irreversible Transactions: Once a transaction is confirmed on the blockchain, it cannot be reversed, making errors costly.
Fiat Currency
Fiat currency, while stable, also has its drawbacks:
- Inflation: The purchasing power of fiat currency can erode over time due to inflation, especially if central banks print too much money.
- Centralized Control: Governments and central banks have immense power over the money supply, which can be misused or lead to economic instability.
- Seizure and Censorship: Funds held in traditional banking systems can be frozen or seized by authorities.
- Transaction Fees and Delays: International transfers can be slow and expensive due to intermediary banks.
- Economic Crises: Fiat currencies are susceptible to economic downturns, recessions, and hyperinflation if not managed properly.
Tools, Examples, and Comparisons
To further illustrate the difference between cryptocurrency and fiat currency, let’s compare them across several key aspects:
| Feature | Cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) | Fiat Currency (e.g., USD, EUR) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuing Authority | Decentralized network (miners/validators) | Central banks and governments |
| Underlying Value | Network consensus, supply/demand, utility, trust in technology | Government decree, trust in government, economic stability |
| Transaction Speed | Varies widely (seconds to minutes), depends on network congestion | Generally fast for domestic digital transactions, slower for international |
| Transaction Cost | Varies (gas fees), can be high during peak network usage | Varies (bank fees, transfer fees), generally lower for domestic transactions |
| Anonymity/Privacy | Pseudonymous (transactions are public but linked to addresses, not identities) | Generally low (transactions linked to identities via banks) |
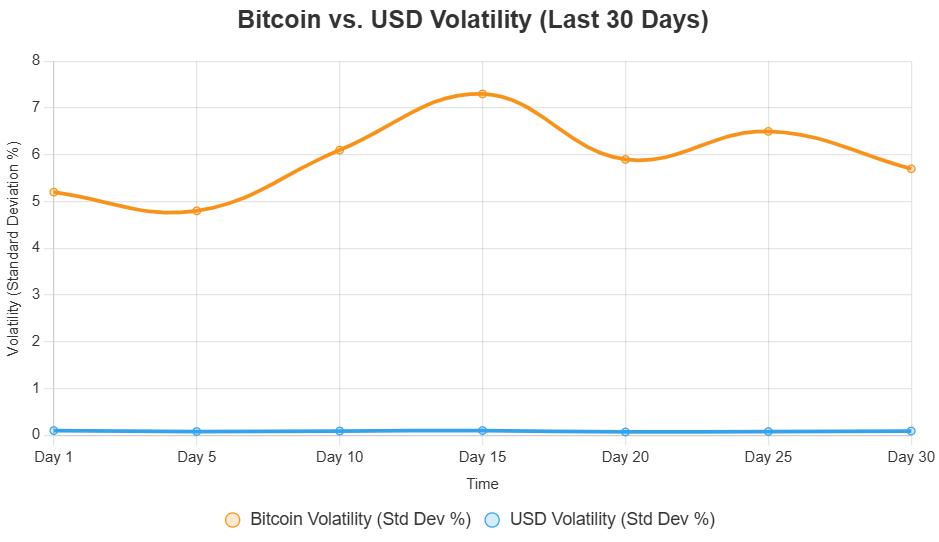
| Volatility | High | Low (relative to crypto), but susceptible to inflation |
| Accessibility | Internet connection and digital wallet required | Bank account, physical cash, or digital payment systems required |
| Regulation | Evolving, often fragmented | Highly regulated and established |
Examples of Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), Ripple (XRP), Litecoin (LTC), Cardano (ADA).
Examples of Fiat Currencies: United States Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Chinese Yuan (CNY).
Final Thoughts and Summary
The difference between cryptocurrency and fiat currency is profound, reflecting two fundamentally different approaches to money and finance. Fiat currency, with its centralized control and government backing, offers stability and widespread acceptance, making it the bedrock of our current global economy. However, it is susceptible to inflation and government policies. Cryptocurrency, on the other hand, represents a decentralized, transparent, and innovative alternative, offering financial inclusion and potential for high returns, but also carrying significant risks related to volatility and regulatory uncertainty.
For US investors, understanding these distinctions is paramount. Whether you choose to invest in digital assets, rely solely on traditional money, or adopt a hybrid approach, being informed about the characteristics, benefits, and risks of both is key to making sound financial decisions in an increasingly digital world. The future of money may well involve a blend of both, leveraging the strengths of each to create a more robust and inclusive financial system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is cryptocurrency legal in the USA?
Yes, cryptocurrency is legal in the USA, but it is regulated differently depending on the state and the specific type of cryptocurrency. The IRS treats cryptocurrency as property for tax purposes, and various federal agencies are developing regulatory frameworks.
Q2: Is fiat currency backed by anything?
No, fiat currency is not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver. Its value is derived from government decree and the public’s trust in the issuing government and its economic stability.
Q3: Which is safer, cryptocurrency or fiat currency?
Fiat currency is generally considered safer due to its stability, government backing, and established regulatory frameworks. Cryptocurrency, while offering potential for high returns, carries higher risks due to its volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and susceptibility to hacks and scams.
Q4: Can I convert cryptocurrency to fiat currency?
Yes, you can convert cryptocurrency to fiat currency through various cryptocurrency exchanges. These platforms allow you to sell your crypto for USD or other fiat currencies, which can then be withdrawn to your bank account.